Celebrate the Caribbean Endemic Bird Festival (CEBF) with us! Our theme in 2023 is “Water: Sustaining Bird Life,” highlighting the importance of water conservation to both humans and birds. Have fun learning about a new endemic bird every day. We have colouring pages, puzzles, activities, and more. Download for free and enjoy nature with your family at home.
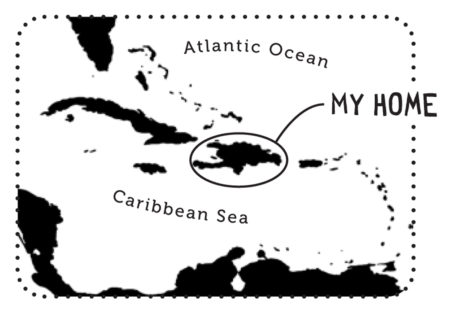
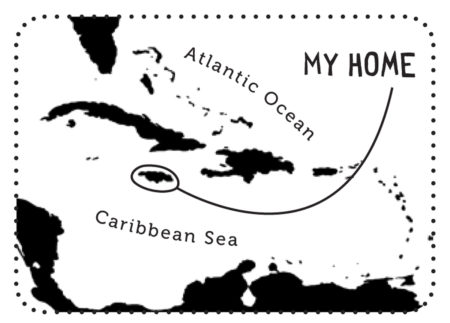
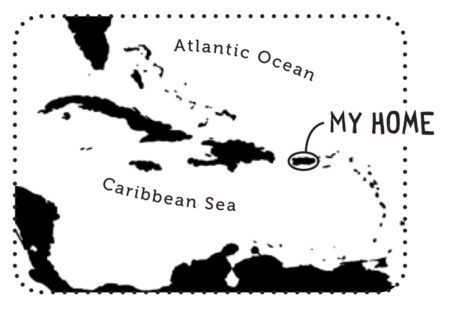
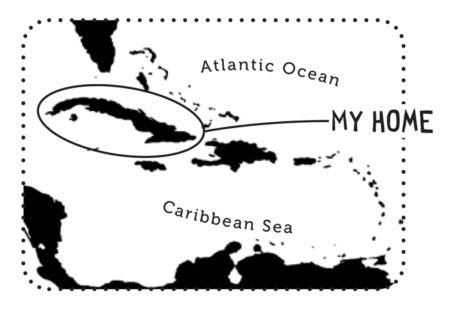
Endemic Bird of the Day: Martinique Oriole
Orioles in the Lesser Antilles have black heads and necks, but not the Martinique Oriole! It stands out from the others by having a dark cinnamon hood. Its underparts, rump, and epaulets (shoulders) are a burnt-orange, and wings, back, and tail are black. Looking at the base of the lower bill you will notice that it is actually pale bluish-gray in color. Sexes are alike but the female is a bit duller.
Even though it is brightly colored the Martinique Oriole is still easy to miss. This is because it spends its time foraging in the canopy above for insects, flowers, and fruits. Additionally it has a restricted distribution on the island. Its main habitats include mangroves, dry forest on limestone soils, humid forest, gardens and tree plantations below 700m. Listen out for its song of clear whistles and soft warbles as well as harsh, scolding calls “cheeu.”
Breeding generally occurs from February to July, but has been reported in December too. They weave palm fibers into a shallow pendant basket nest usually 2–4 m above the ground. The nest is attached or stitched to the underside of a large leaf of tree, e.g., seagrape or trumpet tree, to a palm frond, or to the leaf of banana or Heliconia plant. Clutch size is 2–3 eggs that are white to pale bluish with brown spots and blotches. The incubation period lasts a minimum of 14 days. Both male and female feed the chicks and defend the nest.
Its restricted distribution, as well as population decline, have been attributed to brood parasitism by the Shiny Cowbird and deforestation. The Shiny Cowbird will lay her eggs in the nests of other birds and let the other mother bird, in this case the Martinique Oriole, do all of the hard work of incubating and rearing the young cowbirds.
The Martinique Oriole is considered Vulnerable with a decreasing trend in population size and small global range. However, a recent decrease in cowbird numbers has allowed a slight recovery. The species will also benefit from the protection of its preferred habitats from being destroyed and replaced by agriculture, housing, resorts and other businesses. Learn more about this species, including its range, photos, and calls here.
Colour in the Martinique Oriole
Download our West Indies Endemic Bird colouring page. Use the photos below as your guide, or you can look up pictures of the bird online or in a bird field guide if you have one. Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #CEBFfromthenest
Listen to the song of the Martinique Oriole
The song of the Martinique Oriole is a series of clear whistles.
Puzzle of the Day
Click on the image below to do the puzzle. You can make the puzzle as easy or as hard as you like – for example, 6, 8, or 12 pieces for young children, all the way up to 1,024 pieces for those that are up for a challenge!


Activity of the Day
 FOR KIDS: Can you find the words in our Martinique Oriole word search? Remind yourself of some of the interesting facts about this endemic bird as you look for all 15 hidden words! Remember the words appear forwards and backwards, as well as horizontal, vertical and diagonal! Need some help? Or want to check your answers? You can see where all the words were here.
FOR KIDS: Can you find the words in our Martinique Oriole word search? Remind yourself of some of the interesting facts about this endemic bird as you look for all 15 hidden words! Remember the words appear forwards and backwards, as well as horizontal, vertical and diagonal! Need some help? Or want to check your answers? You can see where all the words were here.
FOR KIDS AND ADULTS: Enjoy this video of a Martinique Oriole in the wild!






















































![PIPLFW[YA]andFL[8P]CINSnorthbeach-Patrick-Leary Banded Piping Plovers](https://i0.wp.com/www.birdscaribbean.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/PIPLFWYAandFL8PCINSnorthbeach-Patrick-Leary.jpg?w=400&h=287&ssl=1)