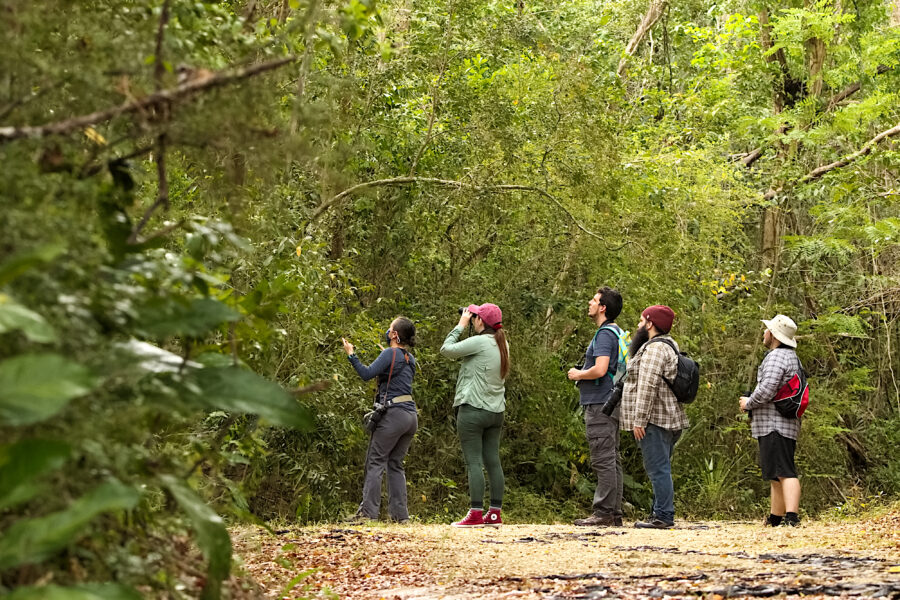
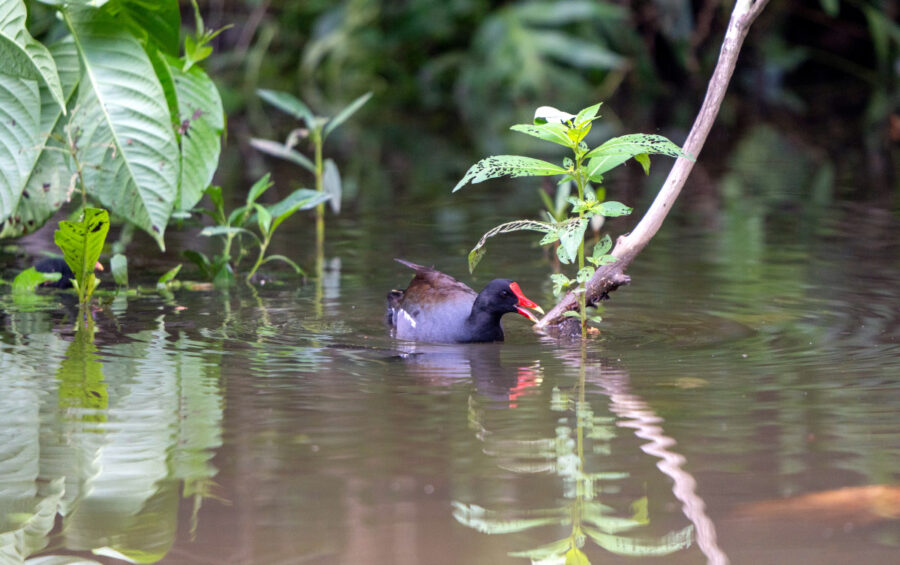
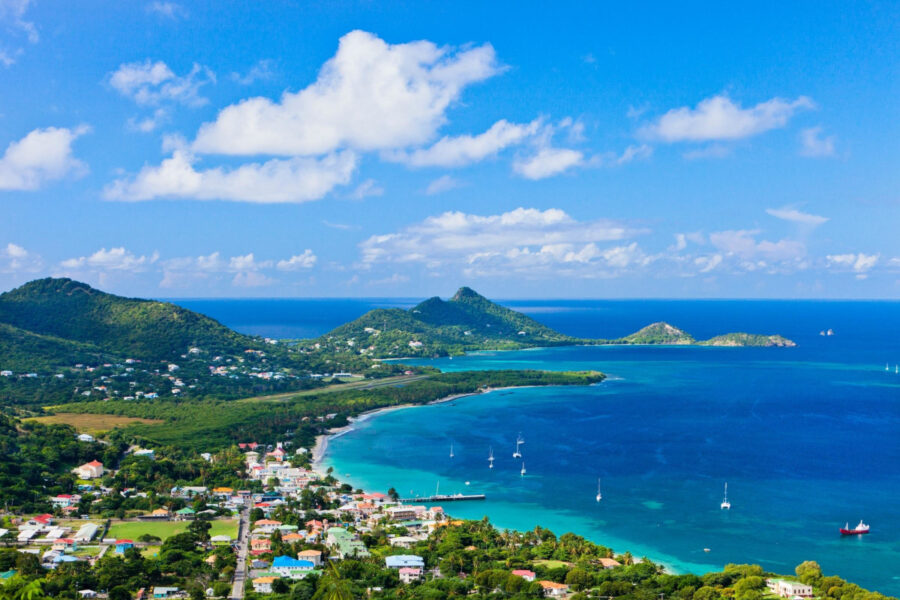
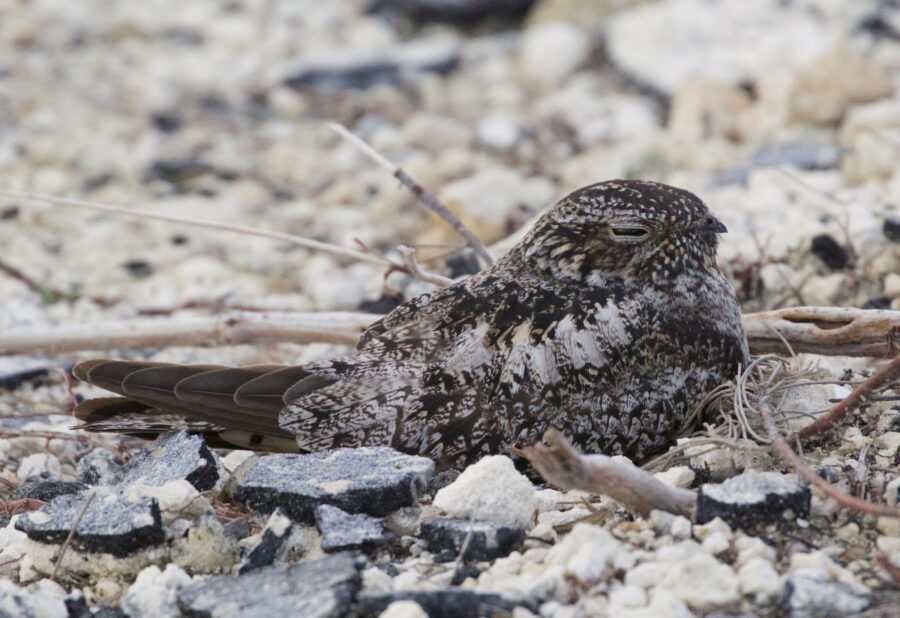
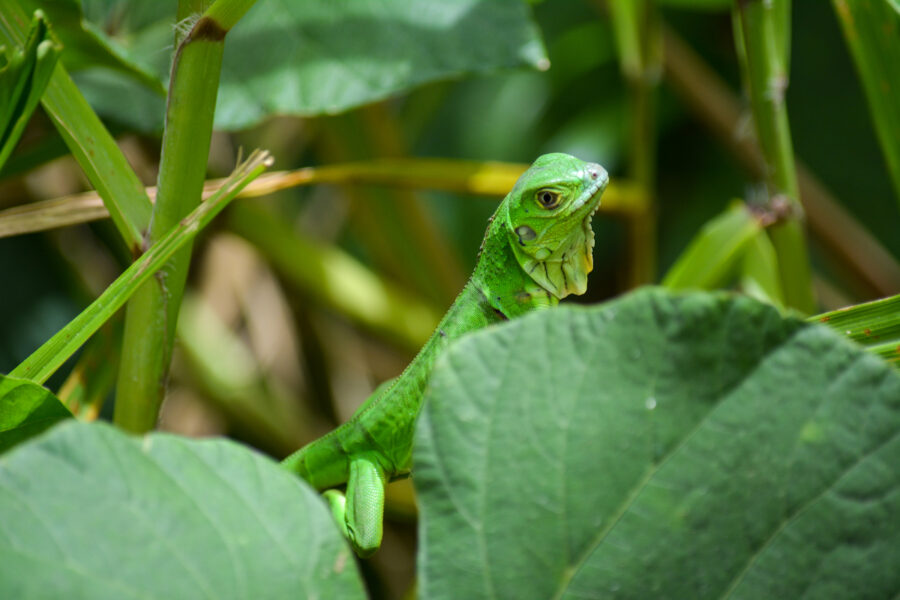
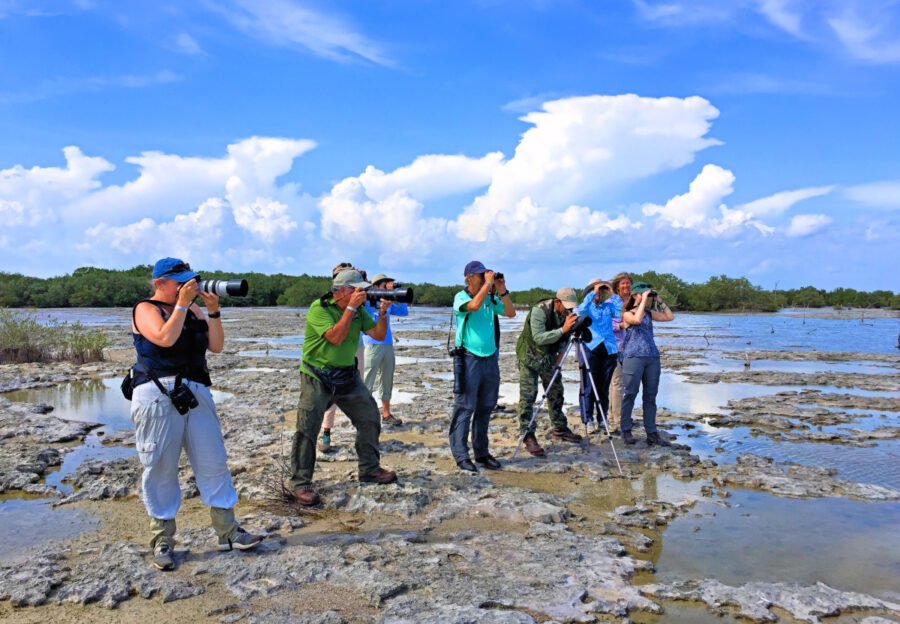
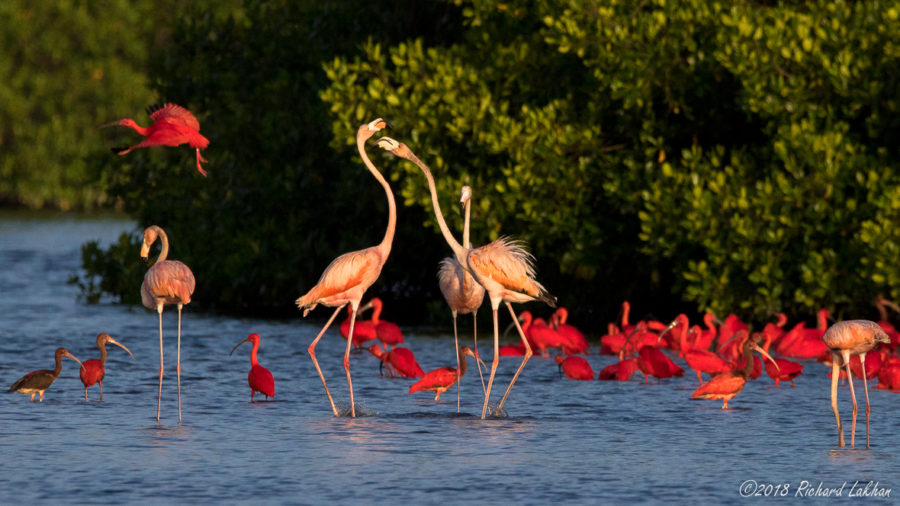
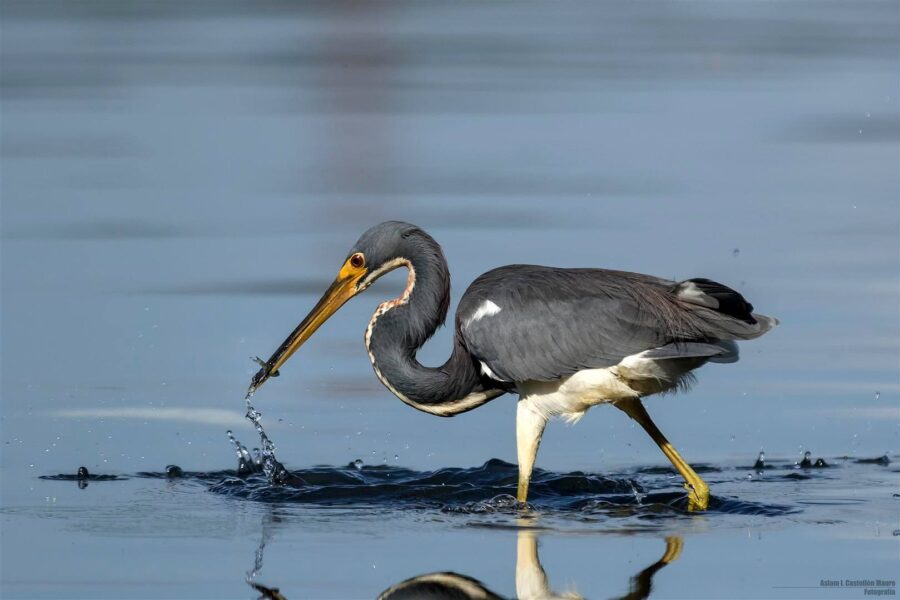
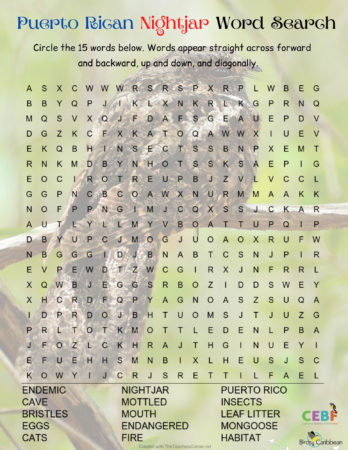
It’s here at last! We are thrilled to announce the recent publication of the highly anticipated, one-of-a-kind Birds of the Lesser Antilles field guide.
The author, Ryan Chenery, is the Barbados-born director of Birding the Islands – a locally owned and operated birding tour company specializing in organizing and delivering both single and multi-island bird tours throughout the Lesser Antilles.
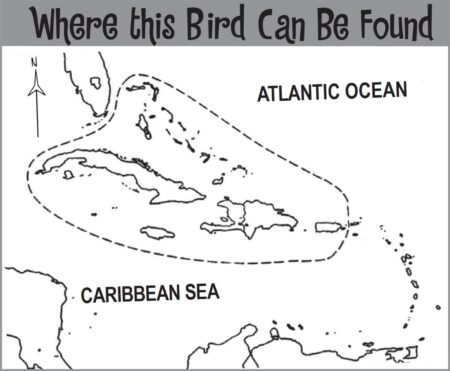
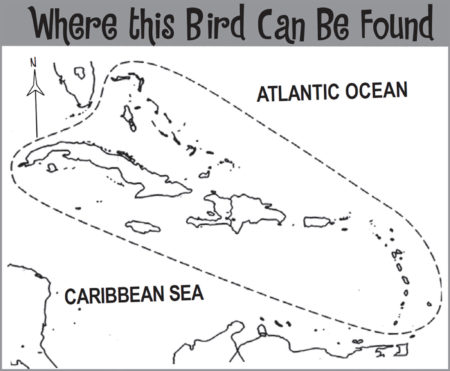
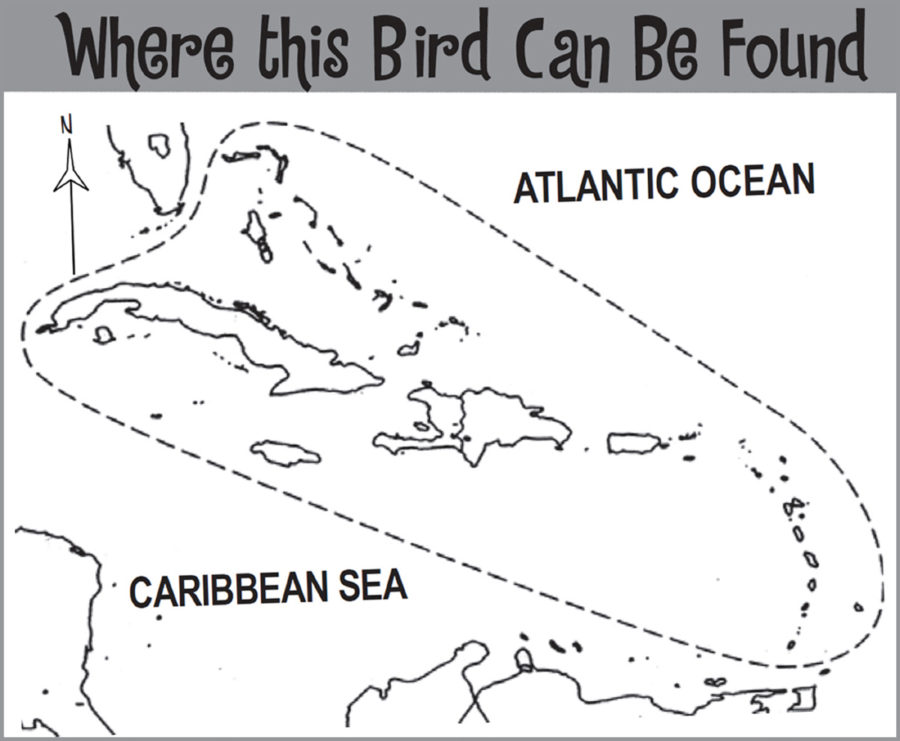
Popular holiday destinations such as St. Lucia, Dominica, Barbados, Guadeloupe, and the other islands dotted along this south-easterly region of the Caribbean now have a comprehensive bird field guide dedicated exclusively to them. Previously these islands have tended to be incorporated into all encompassing Birds of the West Indies field guides. Drawing on over twenty years of experience, the author focuses solely on species that can be seen in the Lesser Antilles. By excluding species unique to other islands in the wider Caribbean region – this field guide allows readers to easily identify all the birds they could possibly find, from Anguilla in the north of the chain to Grenada in the south.
Some important features of this exciting new book are:
-
- The full list of islands covered is as follows: Anguilla; Saint Martin; Sint Maarten; Antigua and Barbuda; St. Kitts and Nevis; Montserrat; Guadeloupe; Dominica; Martinique; St. Lucia, Barbados, St. Vincent and the Grenadines; and Grenada.
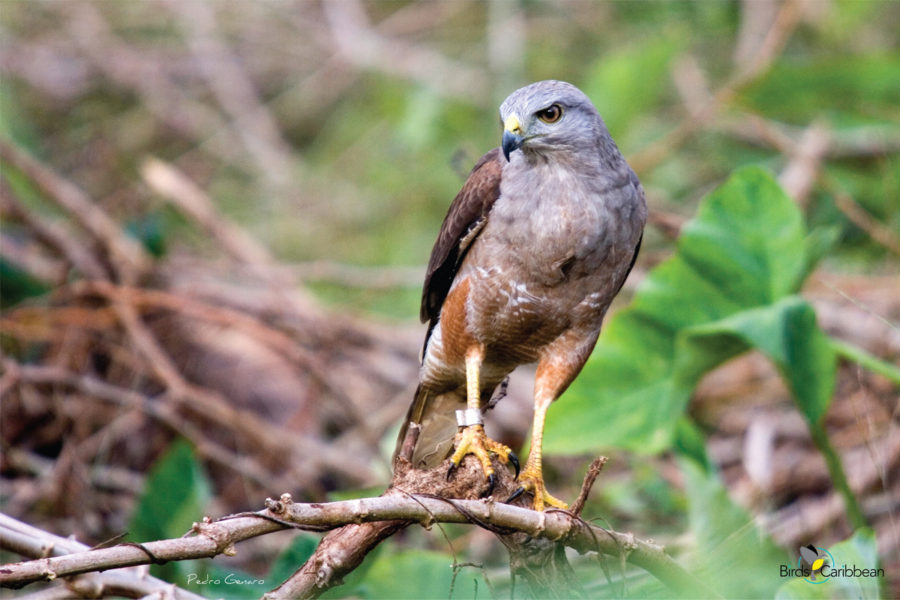
- Each of the field guide’s more than 400 stunning photos has been carefully selected to highlight the key identifying features of each species. Photos include perched birds and those in flight, and importantly also depict notable differences in gender, age and breeding status.
- Special attention has been paid to endemics, near-endemics, and the host of regional specialties unique to the islands of the Lesser Antilles – with notable attention even being paid to detailing differences between subspecies on various islands.
- With the region such a rich area for migratory birds, the publication includes every migrant species likely to be seen, along with the most commonly recorded vagrants and introduced species.
- In clear and helpful language, the key physical characteristics of each species are described to assist with accurate identification. Vocalizations are also included in each species account, along with the island where the bird can be seen.
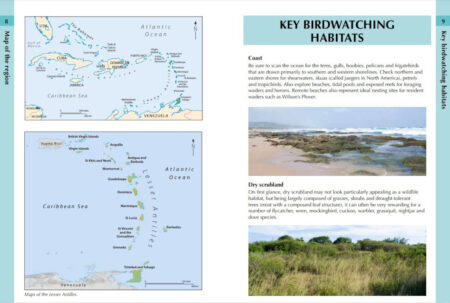
- The best birding locations, key habitats to focus on and the likely species to be encountered in each location are also detailed. From marine and coastal habitats to wetlands and montane forest – this book covers them all.
click each image to enlarge
The islands of the Lesser Antilles are rapidly becoming more popular in the birding community, as well as with holiday visitors. If you are planning a trip to any of these remarkable small islands, whether for a holiday or any other reason, you just have to pack this highly portable guide in your bag!
If you find yourself on an island in the Lesser Antilles, staring at a bird….odds are you’ll find it in the pages of this book!
 About the author: Born in Barbados, Ryan (aka the Bajan Birder) has been leading birding tours in the Caribbean for nearly two decades and is Birding the Islands’ head birding guide. Before starting the company in 2017, Ryan combined leading his birding excursions with a full-time career in conservation. During this time, he was employed as Chief Naturalist and Eco-guide Manager at Graeme Hall Nature Reserve in Barbados; Environmental Consultant for PAA Management Ltd, Barbados; Field Researcher with Global Vision International in the Ecuadorian Amazon; Development Officer with the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) at one of its flagship reserves in the UK; and finally Parks Officer with North York Moors National Park in North Yorkshire, UK. Ryan leads Birding the Islands’ Every Endemic trips through the Lesser Antilles and Trinidad, as well as Endemics of the Solomon Islands tours, but still enjoys branching off to do other projects – including authoring this guide book, and writing episode scripts for a US Fish and Wildlife Service and Canadian Wildlife Service Nature Documentary on shorebird migration through the Lesser Antilles.
About the author: Born in Barbados, Ryan (aka the Bajan Birder) has been leading birding tours in the Caribbean for nearly two decades and is Birding the Islands’ head birding guide. Before starting the company in 2017, Ryan combined leading his birding excursions with a full-time career in conservation. During this time, he was employed as Chief Naturalist and Eco-guide Manager at Graeme Hall Nature Reserve in Barbados; Environmental Consultant for PAA Management Ltd, Barbados; Field Researcher with Global Vision International in the Ecuadorian Amazon; Development Officer with the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) at one of its flagship reserves in the UK; and finally Parks Officer with North York Moors National Park in North Yorkshire, UK. Ryan leads Birding the Islands’ Every Endemic trips through the Lesser Antilles and Trinidad, as well as Endemics of the Solomon Islands tours, but still enjoys branching off to do other projects – including authoring this guide book, and writing episode scripts for a US Fish and Wildlife Service and Canadian Wildlife Service Nature Documentary on shorebird migration through the Lesser Antilles.
We encourage you to visit Birding the Islands website and consider signing up for one of their amazing tours (or build your own tour). Ryan and Birding the Islands are an official partner of our Caribbean Birding Trail program and he donates a portion of the proceeds to BirdsCaribbean from every tour to help conserve Caribbean birds and habitats.
How to get your copy of Birds of the Lesser Antilles:
Available now in stores across the US and Canada. It can be purchased online and delivered worldwide on Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/Birds-Lesser-Antilles-Wildlife-Guides/dp/1472989619
If you are a Kindle reader, the Kindle eBook is available for purchase now and can be read on any device with the free Kindle app.
The field guide is also now available in stores across the UK and for purchase online on Amazon UK: https://www.amazon.co.uk/Birds-Lesser-Antilles-Wildlife-Guides/dp/1472989619
Or directly from Bloomsbury Publishing here: https://www.bloomsbury.com/us/birds-of-the-lesser-antilles-9781472989611/